High Density Plastic is a versatile material with a wide array of applications. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in the field, "High Density Plastic has transformed manufacturing and design." Her statement highlights the immense value this material offers across various industries.
From packaging to construction, High Density Plastic serves crucial roles. It’s lightweight, durable, and resistant to moisture. These properties make it ideal for outdoor furniture, automotive components, and even medical devices. However, challenges remain. The environmental impact of plastic production is significant. Recycling options for High Density Plastic are still developing.
Many industries rely heavily on this material. Yet, it's vital to consider sustainable alternatives. Businesses must reflect on their usage and the life cycle of High Density Plastic. By addressing these concerns, industries can innovate and utilize this material responsibly while minimizing their ecological footprint.
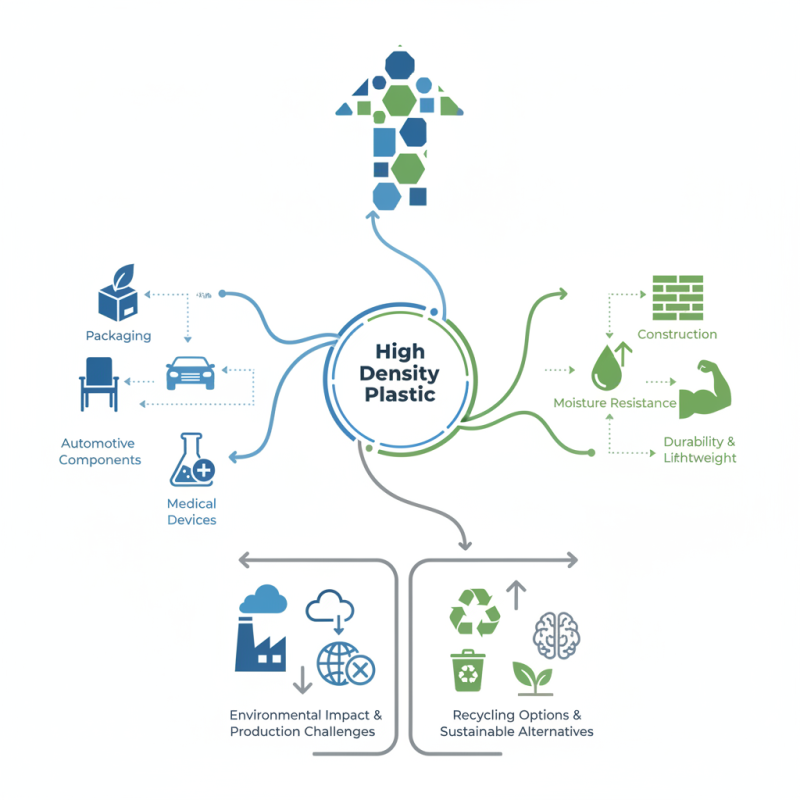
High-density plastic, often abbreviated as HDPE, is a versatile material known for its unique composition and properties. It consists of tightly packed polymer chains, making it stronger and more resilient than other plastics. This density gives HDPE excellent resistance to impact and moisture, making it suitable for various applications like containers, pipes, and even outdoor furniture. Its durability means it can withstand harsh environmental conditions without failing.
When handling high-density plastic, keep a few tips in mind. Choose the right thickness for your application to ensure maximum strength. Thicker materials can provide better durability but may be more challenging to work with. Additionally, ensure proper recycling practices. HDPE is widely recyclable, but contamination can hinder this process.
Remember, not all HDPE products are created equal. Some may have varying levels of UV resistance. If a product will be exposed to sunlight, consider this factor. It’s essential to reflect on whether your choice of high-density plastic will meet your specific needs over time. Not appreciating these details can lead to potential frustrations down the road.
High-density plastic, known for its strength and durability, finds extensive use in various applications. In industries such as automotive and packaging, its resistance to impact and chemicals makes it a preferred choice. Research shows that high-density polyethylene (HDPE) can withstand temperatures up to 120°C, making it ideal for outdoor products that need to endure harsh environments.
When we talk about benefits, let's consider its lightweight nature. This characteristic contributes to reduced shipping costs. According to industry reports, companies can save up to 20% on transportation by using HDPE compared to heavier materials. Notably, its impermeability makes it suitable for carrying liquids without leakage, which is crucial for safety.
Tips: Opt for high-density plastic for containers that deal with corrosive chemicals. This choice can prolong product life. Remember to evaluate the specific material grade for your needs. Not all high-density plastics are created equal; some may not meet specific industry standards. A thoughtful choice in material can prevent future issues, as using the wrong type can lead to material breakdown or failure in critical applications.
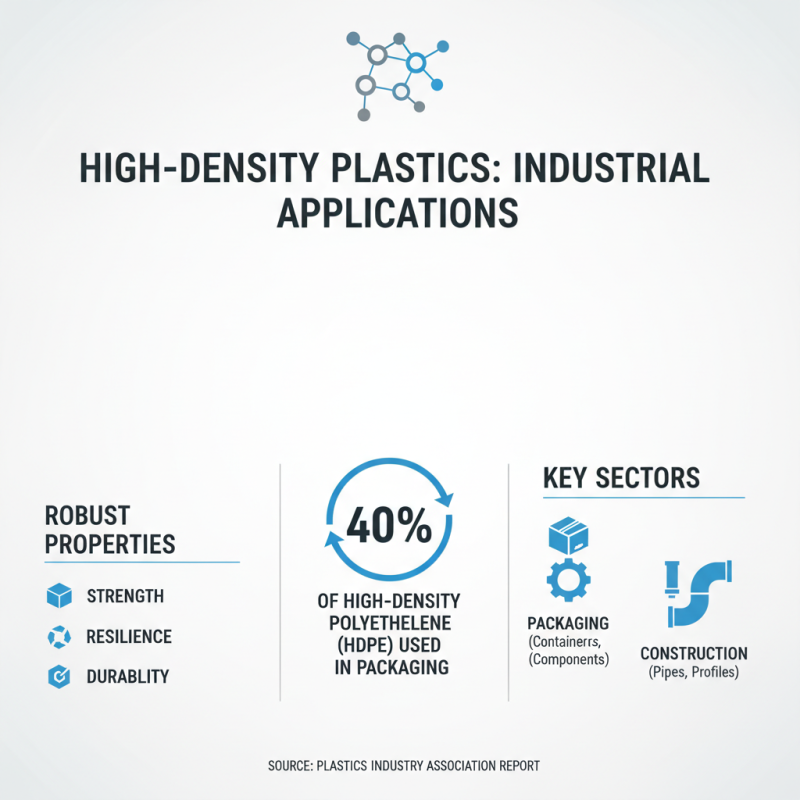
High-density plastic materials are highly regarded in various industrial and commercial sectors. Their robust properties make them ideal for applications requiring strength and resilience. For instance, the packaging industry extensively uses these plastics for containers and protective wraps. According to a report from the Plastics Industry Association, over 40% of high-density polyethylene is utilized in packaging alone.
In the automotive sector, high-density plastics serve crucial roles. They are used in manufacturing parts like dashboards and interior components. A study by the American Chemical Council found that lightweight plastic parts can reduce vehicle weight by up to 20%. However, the challenge is ensuring durability and resistance to impacts while maintaining a lightweight design. Manufacturers often grapple with balancing these factors.
The construction industry also benefits greatly from high-density plastics. They are used in pipes, insulation, and protective coatings. However, the environmental impact raises concerns. There’s a growing need for sustainable practices in sourcing and recycling these materials. Many companies struggle with creating a closed-loop system that minimizes waste. It's a critical point that needs more focus as industries evolve.
High density plastics (HDPE) are widely used due to their durability and versatility. However, their environmental impact is significant. When improperly disposed of, HDPE can persist in landfills for decades. This creates waste that harms ecosystems and wildlife.
Recycling is essential for reducing the impact of HDPE. Many recycling facilities accept this type of plastic. However, contamination in recycling streams can complicate the process. Even small amounts of food residue or mixed materials can lead to entire batches being rejected.
Education and awareness are vital. They can help improve recycling rates. Consumers need to understand the right ways to dispose of HDPE products. Simple actions like rinsing containers can make a big difference. Yet, only a fraction of HDPE is recycled. This calls for more robust systems and innovative solutions to enhance recycling efforts.
| Application | Description | Environmental Impact | Recycling Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Packaging | Used for food containers, bottles, and other consumer goods. | Can take hundreds of years to decompose; potential ocean pollution. | Can be recycled into new products or energy recovery processes. |
| Construction | Used for pipes, fittings, and geomembranes. | Durability can lead to extended life cycles; energy-intensive to produce. | Recyclable, but often not recycled due to contamination and logistics. |
| Automotive | Used in dashboards, door panels, and interior components. | Contributes to vehicle weight reduction, improving fuel efficiency. | Recycling programs exist to recover materials from end-of-life vehicles. |
| Consumer Goods | Includes toys, household items, and electronics. | Potential for pollution if not disposed of properly. | Many products can be recycled; check local programs. |
| Medical Devices | Used for syringes, IV bags, and surgical tools. | Single-use impacts waste management; critical for sterility. | Specialized recycling programs available for medical plastics. |
High-density plastic is becoming increasingly versatile in its applications. Industries are exploring advanced methods for its production and usage. The future seems promising. Innovations in recycling methods are reshaping how we view plastic. Many believe that high-density plastic could be fully renewable.
New technologies are allowing for more eco-friendly variants of high-density plastic. Biodegradable options are emerging, yet questions remain about their efficiency. The demand for sustainable materials is clear, but the industry struggles with implementation. There’s also the challenge of performance; these plastics must meet rigorous standards.
In packaging, high-density plastics support a variety of needs. Lightweight and durable, they help reduce shipping costs. However, we must ask ourselves, are we truly minimizing waste? New ideas around closed-loop systems are developing, advocating for responsible usage. It’s crucial to assess both the benefits and drawbacks as we innovate. The balance is delicate, and continuous reflection is necessary for progress.